Definition
Situation where normal alignment of carpal bones is lost
Aetiology
- DISI
- due to disruption of scapho-lunate articulation
- VISI
- secondary to disruption of lunate & triquetral
- Ulnar translocation
- rarely results from injury but is commonly seen in wrists affected by rheumatoid arthritis
Epidemiology
Anatomy
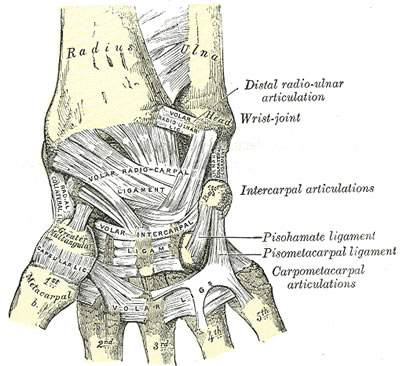
- Two major groups of ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments course between carpal bones & radius or metacarpals
- intrinsic ligaments originate & insert in carpus
- extrinsic ligaments are stiffer while intrinsic ligaments are capable of greater elongation before permanent deformation occurs
Extrinsic
Palmar
- palmar extrinsic ligaments consist of 2 V-shaped ligamentous bands
- one is proximal & connects forearm to proximal carpal row
- proximal limb consists of
- radiolunotriquetral & radioscaphoid ligs laterally
- ulnolunate & ulnotriquetral ligs medially
- proximal limb consists of
- one is distal & connects forearm to distal carpal row
- distal limb of palmar extrinsic ligs consists of
- radioscaphocapitate ligament laterally
- ulnocapitate ligament medially
- distal limb of palmar extrinsic ligs consists of
- one is proximal & connects forearm to proximal carpal row
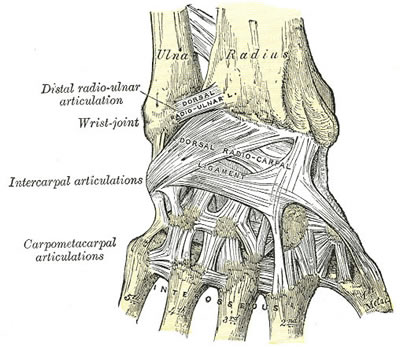
Dorsal
- dorsal extrinsic ligaments
- radiotriquetral
- scaphotriquetral
Intrinsic
- intrinsic ligs connect adjacent carpal bones
- Proximal row
- intraarticular
- connecting scaphoid to lunate & lunate to triquetrum
- strong
- critical for carpal stability
- intraarticular
TFCC
- separates ulna from carpus
- Made up of
- TFC
- dorsal & volar radio-ulna ligaments
- ulnar collateral ligament
- meniscus homologue
- articular disc
- sheath of ECU
- Variable thickness of TFC from 1 – 5mm depending on station of ulna (ulna variance)
- No tendons are directly attached to carpus
- Made up of
Rows/Columns
- Traditional view
- proximal & distal row of carpal bones- scaphoid joining them
- Taliesnik
- three columns
- scaphoid being radial column
- triquetral ulnar column
- lunate & capitate with remaining carpal bones making up middle column
- three columns
- Navarro
- Three column modification
- scaphoid, trapezium & trapezoid making up radial column
- triquetral ulnar column
- capitate & lunate along with hamate middle column
- Three column modification
Pathology
Classification
4 major types of carpal instability
- DISI:
- Dorsi-flexion (Dorsal Intercalated Segment Instability)
- most common where lunate is rotated into dorsi-flexion
- (zig zag alignment of radiolunatocapitate alignment)
- VISI:
- Palmar flexion (Volar Intercalated Segment Instability or VISI)
- Ulnar Translocation
- abnormal translocation of lunate ulnarward
- Type 1 entire carpus is translocated ulnarward
- Type 2 relationship between radius & scaphoid is normal but scapholunate gap is wide
- rheumatoid
- abnormal translocation of lunate ulnarward
- Dorsal Subluxation
- malunion fracture distal radius with reversal of normal palmar tilt
Instabilities may be
- Static
- loss of normal alignment can be seen on XR
- Dynamic
- routine XR within normal limits
- instability can be produced by either voluntary movement or manipulation
- eg between scaphoid + lunate, between lunate + triquetrum, or at midcarpal joint
Instabilities may also be termed
- Dissociative
- S-L dissocation DISI
- L-T dissociation VISI
- Nondissociative
- may also result in VISI or DISI but 3 bones (S,L,T) act as unit
- eg dorsal carpal subluxation, mid-carpal instability, Type1 ulnar translocations
History
Examination
- painful wrist
- clicking or clunking
- Ballottement test
- Watson test for scaphoid instability
Investigations
- AP
- AP wrist under axial load (clenched fist)
- hand in radial & ulnar deviation
- Findings
- May demonstrate distance between scaphoid & lunate or lunate & triquetral
- DISI pattern
- scapholunate gap
- ring sign
- with flexed scaphoid seen end on
- scaphoid foreshortened
- distance between ring & proximal pole less than 7mm
- flexed scaphoid is seen with dorsiflexed lunate
- (quadrilateral) & with triquetrum in distal (dorsiflexed) position
- VISI pattern
- ring sign
- scaphoid foreshortened
- lunate volar flexed (triangular)
- triquetrum distal in relation to hamate ( dorsiflexed)
- distance between ulnar head & triquetrum is reduced ( Mayersbach sign)
- convex outline of proximal carpal row (= Shentons line of wrist) is interrupted by step off between lunate & triquetrum
- Ulnar Translocn
- Carpal-Ulnar distance
- is distance from centre of head of capitate ( ie centre of rotation of carpus) & line produced along line of centre of ulna
- Normally ratio of C-U distance/ length of 3rd metacarpal = .30 ± .03
- ¯ in ulnar translocation
- Carpal-Ulnar distance
- Lat: to assess opposite rotations of scaphoid & lunate
- DISI pattern
- when scapholunate joint is dissociated
- scaphoid is palmar flexed
- lunate is dorsiflexed
- Scapho-lunate angle
- Normal 30- 60° (av 46o)
- DISI > 70°
- when scapholunate joint is dissociated
- VISI pattern
- lunate palmar flexed
- lunotriquetral angle
- Normal -16 deg
- Abn neutral or +ve
- Ulnar Translocation
- often associated with VISI
- SLAC wrist (scapho-lunate advanced collapse)
- With S-L dissocation
- All load going through Radioscaphoid joint
- degenerative process
- radial styloid & scaphoid
- luno-capitate joint (commonest pattern of degeneration 55%)
- triscaphoid degeneration
- between scaphoid, trapezium + trapezoid
- 2nd most common pattern
- With S-L dissocation
- Other Ixs
- Bone scan
- is useful to identify pathology
- When bone scan is negative it suggests either that there is no injury or more frequently that problem is minor & can be treated non operatively
- Arthrography
- is helpful in finding ligament tears but ? significance as these may not necessarily be result of trauma but may indicate age related degenerative change
- NB: need to compare with normal side
- Arthroscopy
- can directly visualise pathology
- Bone scan
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- of chronic instability depends on patients symptoms
- Nonsurgical
- little disability
- > 80% of ROM
- > 80% grip strength
Scapholunate dissociation
- Acute
- either closed manipulation or open reduction with pinning
- Chronic: if no associated Osteoarthritis
- reattachment of scapholunate ligament
- dorsal capsuloligamentodesis (Blatt)
- dorsal capsular flap used to prevent scaphoid from subluxing in palmar direction
- ref : Blatt & Nathan ” Dorsal Capsulodesis for rotatory subluxation of scaphoid: review of long term results” Proc Am Soc of Surgery of Hand 1992
- STT fusion
- problem is with radial impingement
- S-L or S-C fusion
- if associated Osteoarthritis ( ie SLAC )
- Excise (?replace) scaphoid & perform mid carpal fusion that is fusion of capitate, hamate, triquetral & lunate
- (= 4 – corner fusion)
- total wrist fusion
Lunatotriquetral instability
- Acute
- either immobilisation in BEPOP or direct repair of ligament
- chronic
- Lunatotriquetral arthrodesis
Ulnar Translocation
- Acute
- Repair of disrupted volar & dorsal radiocarpal ligs
- Chronic
- ligament repair unreliable
- relocation of carpus & maintenance of reduction by radiolunate arthrodesis more reliable
Dynamic VISI & DISI
- trial of nonoperative management with AEPOP/ NSAIDS/ local injection of steroids
- Stabilisation of midcarpal joint limited fusion
- Capsuloligamentodesis
- tenodesis